Empty cart?
We can only assume that's because you haven't seen our latest offers
We use cookies to facilitate your website usage, improve our products, and tailor them to you. Together with other Vision Healthcare companies, we provide you with personalised offers. You have control over which cookies you want to allow or reject. You can revoke or change your consent at any time. Further information and details can be found in the privacy policy.
Cookies are used on this website, as is the case on most other websites. We use cookies to give you a good user experience. A cookie is a small file that typically contains a sequence of letters and numbers that are loaded on a user's computer or mobile phone when you visit a Web site.
Cookies help us:
We do not use cookies for:
Learn more about the cookies that are active on this site.
By accessing this website with your browser, this means that you accept cookies and that you agree to their use. If you do not use the cookies on this website, please continue reading. However, blocking the cookies may cause the site to function only sub-optimal.
First-party cookies
We use cookies to optimize the performance of websites that include the following:
These cookies will not function other than by visiting this website.
Other Cookies
Other cookies come from other partners. An example for other cookies would be the integration of Youtube video on our website. Our website contains the following places of origin of the so-called other cookies:
Blocking or removing these cookies can very likely lead to blocking or non-viewing the content of this site.
| Submitted by | Name | Restriction | Description |
| sensilab.com | popup_displayed | Sessions | Means that the display opens |
| sensilab.com | frontend | Sessions | Session ID |
| sensilab.com | cookieOK | 1 year | Means that the user on a site agrees with the use of cookies |
| sensilab.com | popups | 1 year | |
| sensilab.com | external_no_cache | Sessions | System cookies to optimize servers |
| sensilab.com | cookieOK | 1 year | |
| sensilab.com | user_allowed_save_cookie | 1 year | Means that users agree to the transfer of cookies to the site |
| sensilab.com | zte2095 | Sessions | Cookie allows chat |
| sensilab.com | __zlcmid | 1 year | Cookie allows chat |
| CloudFlare | __cfduid | 1 year | For a faster location and transfer of image material on the page. After CloudFlare disable the operation cookies block access via IP. Does not use / has no personal data of the user. |
| New Relic | bam.nr-data.net | Sessions | New Relic provides a platform to control the operation of the website on mobile applications. |
| PayPal | [various] | Sessions | This cookie allows a unique ID between payment with PayPal and our shopping cart. |
Their goal is to simplify sharing and to integrate our content into social networks such as Facebook and Twitter.
Cookies are set up:
Privacy policy depends on each social network and works on your personal account of the network based on the settings.
| Submitted | Name | Restriction |
| Addthis | uvc | Sessions |
| Addthis | page_services | indefinitely |
| Addthis | vc | 2 years |
On this page we regularly test new motifs. We do this to show different motifs for different user groups. In this way, we test the responsiveness of users in a variety of creativity and content. Only then can we land with the best.
Use:
| Submitted | Name | Restrictions |
| Optimizely | optimizelyPendingLogEvents | Sessions |
| Optimizely | optimizelyBuckets | Permanent |
| Optimizely | optimizelyEndUserId | Permanent |
| Optimizely | optimizelySegments | Permanent |
| Optimizely | bucket_map | Permanent |
| Optimizely | end_user_id | Permanent |
We use cookie statistics on this page to determine how many users have visited us, what kind of tools they have used (Mac and Windows - with this we can see where our site does not work as it does in a variety of environments), the pages you see, and the like. With these programs, we can still improve your user experience. Such an analysis also provides a better insight into how users come to our side and whether they are coming back. On this basis, we can invest in the improvement and development of the user experience for you rather than in marketing activities.
Use:
| Submitted | Name | Restriction |
| _gat | Sessions | |
| _ga | 2 years | |
| __utma | 2 years | |
| __utmb | Sessions | |
| __utmz | 6 Months | |
| __utmv | 2 years | |
| __utmc | Sessions |
https://business.safety.google/privacy/
We also use technology that allows us to determine the users who called us (e.g., a browser or ad with the phone number you clicked). In this way, we can get information about how people come to us. Please note that if you call us at the telephone number displayed on our website, we will only know to a certain extent how you found us. All of this will allow us to reduce the costs for you.
Cookies for marketing activities. Cookies are widely used in digital marketing. Through it, neither we nor our external partners can receive personal information from you.
We do not recommend blocking the vast majority of cookies as ads provide free use of the sites. If you block cookies, it means not only that you will not see any ads, but also that the site can no longer be optimized for your wishes and interests, which reduces usability. Cookies have a technology that allows us to accurately and with your help the so-called "remarketing cookies" & rdquo; when you visit certain websites. These ads are designed so that you can buy a product at a reduced price. And do not worry, the process is void anonymous. You may block cookies at any time, as described below.
We use:
List of promotional cookies set on our pages:
| Submitted | Name | Restriction | Description |
| Adform | C | 1 Month | Targeting/Advertising |
| Adform | cid | 2 Months | Targeting/Advertising |
| Adform | uid | 2 Months | Targeting/Advertising |
| AppNexus Inc | sess | Sessions | Targeting/Advertising |
| AppNexus Inc | anj | 3 Months | Targeting/Advertising |
| AppNexus Inc | uuid2 | 3 Months | Targeting/Advertising |
| Bing | ANONCHK | Sessions | Targeting/Advertising |
| Bing | MR | 6 Months | Targeting/Advertising |
| Bing | MUID | 2 years | Targeting/Advertising |
| test_cookie | Sessions | Targeting/Advertising | |
| id | 2 years | Targeting/Advertising | |
| Gravity | gr_reco | 1 year | Targeting/Advertising |
| Improve Digital | tuuid | 2 years | Targeting/Advertising |
| Improve Digital | um | 2 years | Targeting/Advertising |
| Improve Digital | umeh | 2 years | Targeting/Advertising |
| IPONWEB | c | 2 years | Targeting/Advertising |
| IPONWEB | tuuid | 2 years | Targeting/Advertising |
| Media Innovation Group | id | 1 Month | Targeting/Advertising |
| Media Innovation Group | mdata | 1 Month | Targeting/Advertising |
| Media Innovation Group | syncdata_AN | 1 Month | Targeting/Advertising |
| Mojn | idt | Permanent | Targeting/Advertising |
| Mojn | tmpagid | Permanent | Targeting/Advertising |
| Mojn | ls | Permanent | Targeting/Advertising |
| Mojn | rtt | Permanent | Targeting/Advertising |
| Mojn | _mojn | Permanent | Targeting/Advertising |
| OpenX | i | 1 year | Targeting/Advertising |
| Pubmatic | KRTBCOOKIE_466 | 3 Months | Targeting/Advertising |
| Pubmatic | PUBMDCID | 3 Months | Targeting/Advertising |
| RadiumOne | RA1balancer | Permanent | Targeting/Advertising |
| RadiumOne | ra1_sgm | 1 year | Targeting/Advertising |
| RadiumOne | ra1_sgm_1097308745 | 1 year | Targeting/Advertising |
| RadiumOne | ra1_sgm_1118270538 | 1 year | Targeting/Advertising |
| RadiumOne | ra1_sgm_1426802167 | 1 year | Targeting/Advertising |
| RadiumOne | ra1_sgm_1702745841 | 1 year | Targeting/Advertising |
| RadiumOne | ra1_sgm_1795933472 | 1 year | Targeting/Advertising |
| RadiumOne | ra1_sgm_1973119023 | 1 year | Targeting/Advertising |
| RadiumOne | ra1_sgm_2107935356 | 1 year | Targeting/Advertising |
| RadiumOne | ra1_sgm_328720634 | 1 year | Targeting/Advertising |
| RadiumOne | ra1_sgm_631030195 | 1 year | Targeting/Advertising |
| RadiumOne | ra1_sgm_799597431 | 1 year | Targeting/Advertising |
| RadiumOne | ra1_sid | 1 year | Targeting/Advertising |
| RadiumOne | ra1_uid | 1 year | Targeting/Advertising |
| Rubicon Project | c | Sessions | Targeting/Advertising |
| Rubicon Project | put_1986 | 1 Month | Targeting/Advertising |
| Rubicon Project | put_2760 | 1 Month | Targeting/Advertising |
| Rubicon Project | rpb | 1 Month | Targeting/Advertising |
| Rubicon Project | khaos | 6 Months | Targeting/Advertising |
| Rubicon Project | rpx | 1 Month | Targeting/Advertising |
| Yahoo | B | 2 years | Targeting/Advertising |
| datr | 2 years | Targeting/Advertising | |
| x-src | Sessions | Targeting/Advertising | |
| reg_fb_ref | Sessions | Targeting/Advertising | |
| reg_fb_gate | Sessions | Targeting/Advertising |
Cookies can be turned off manually (here). In this way, you will restrict the functionality of not only this website, but probably most sites.
If you do not wish to accept any of the cookies on this site, click here
The purpose of this privacy policy (hereinafter: policy) is to communicate the purpose and legal basis for the processing of personal data by Sensilab to the customers and visitors of Sensilab websites.
Sensilab d. o. o., Verovškova street 55a, 1000 Ljubljana, SLOVENIA, support@sensilab.com (hereinafter: Sensilab or the company or provider or personal data controller) ensure the protection of your personal data and guarantees safety throughout the business interaction.
At Sensilab, we value your privacy and will always diligently protect your data. This privacy policy may be changed, modified or updated at any time, with no prior warning or notification. By using the provider's website, the user confirms she or he agrees with the changes and modifications.
All our online activities, connected to the collection and processing of data, are in accordance with European legislation (Regulation (EU) 2016/697 on the protection of natural persons with regard to the processing of personal data and on the free movement of such data (The EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)) and Treaty Conventions ETS 108, ETS 181, ETS 185, ETS 189) and national legislation of the Republic of Slovenia (Personal Data Protection Act (ZVOP-1, Ur. l. RS, no. 94/07), Electronic Commerce Market Act (ZEPT, Ur. l. RS, no. 96/09 in 19/15) etc.).
The privacy policy covers the handling of personal information that the provider receives whenever you visit or use a Sensilab website or is shared in another way.
The personal data controller is the company SENSILAB farmacevtska družba d. o. o., Verovškova ulica 55a, 1000 Ljubljana, Slovenia.
At Sensilab, there is an authorised person in charge of data protection that is available at the following e-mail address: dpo@sensilab.com.
If you have any questions regarding the use of this policy or in connection with the exercising of your rights under this policy, please contact the Data Protection Officer through the contact listed below.
|
Company |
JK Group d.o.o., Stegne 27, 1000 Ljubljana, Slovenia |
|
E-mail address |
dpo@jkgroup.si(for GDPR-related issues only) |
Personal data or personal information is all information by which an individual can be identified (such as name, surname, e-mail address, telephone number, etc.).
The controller is a legal entity that determines the purposes and means of processing personal data.
The processor is a legal or private individual who processes personal data on behalf of the controller.
Processing is the collection, storage, access and all other forms of use of personal data.
EEA is the European Economic Area, which consists of all members of the European Union, Iceland, Norway and Lichtenstein.
Personal data is a piece of information that identifies you as an individual. An identifiable natural person is one who can be identified, directly or indirectly, in particular by reference to an identifier such as a name, an identification number, location data, an online identifier or to one or more factors specific to the physical, physiological, genetic, mental, economic, cultural or social identity of that natural person.
The provider, according to purposes as defined in this policy, collects the following personal data:
The controller does not collect personal data unless you enable it or consent to it, for example, when ordering products or services, subscribing to an e-mail newsletter, taking part in a prize game, etc., or when there is a legal basis or a legal interest by the controller for data processing.
One of the ways the controller collects your personal data is with the use of cookies. You can read more about the use of cookies here.
The controller only collects the data that is relevant and necessary for the fulfilment of the purposes for which the data is processed.
The period of data for which the provider stores collected data is further defined in the chapter “Storing personal data” of this Policy.
The provider collects and processes your personal data based on the following legal grounds:
Information is collected when it is necessary for entering into, executing and fulfilling contractual obligations. In this case, providing personal information is voluntary.
If you choose to not provide the company with the necessary personal data, you cannot enter into a contract with them, nor can the company provide the services or supply of products, as the company lacks the information necessary to fulfil the contract.
Data is processed only with your explicit consent. When processing is subject to consent, we will first make sure that you have all the necessary information needed for making a decision. You can withdraw your consent at any time. If you withdraw consent, the company may not be able to provide you with their services or products.
The provider can process data on the grounds of legitimate interest for which the provider is striving, provided that the interests or the fundamental rights and freedoms of the data subject are not overriding. When using legitimate interest, the provider always makes a judgement in accordance with the General regulation on data processing.
When processing data on the grounds of legitimate interest, the user has the right to object to the data processing. You can read more about your rights below.
We process your personal information when we are required to do so by the law that binds us (for example, tax law mandates the retention of invoices). We process the needed information in accordance with the requirements of the law.
The company collects and processes data for the following purposes:
|
Purpose of data processing |
Detailed explanation |
|
Communication regarding services or responding to requests |
Notices to users, responses, resolving complaints, completing satisfaction surveys, etc. Processing is carried out on the basis of a legitimate interest in ensuring effective communication and successful transactions. |
|
Entering agreements and the execution of obligations based on the contract |
Entering and executing the contract with the provider, including the provider's fulfilment of your orders (supply of products and provision of services), communication with you, verification of your payments and fulfilment of other obligations of the provider and/or your obligations. We process personal information on a contractual basis and a pre-contractual relationship. In the event that you do not provide us with all the information necessary for the execution of the contractual obligations, we reserve the right to suspend or cancel the order. |
|
Directly informing customers of special offers, discounts and other content via email or SMS. |
At Sensilab d.o.o. Pursuant to ZEKom-1 (Electronic Communications Act of the Republic of Slovenia, implemented pursuant to Directive 2002/58 / EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 12 July 2002), we inform our customers of our products, services and contents. You may at any time request the discontinuation of such communication and processing of personal data (right of objection). You may terminate such communication at any time via the unsubscribe link in the inbox, or by a written request to the e-mail address dpo@sensilab.com, or by using the following form, www.sensilab.si/dpo. In this case, we process your information based on law. |
|
Direct contact about special offers and other content via e-mail |
Based on your consent, we will notify you of your products, services, discounts and content via e-mail. You may at any time request the discontinuation of such communication and processing of personal data by withdrawing consent. You can withdraw your consent at any time through the contacts listed on www.sensilab.com/contact. |
|
Direct contact about special offers and other content via phone calls and regular mail |
Based on customer consent, we also periodically inform customers about our products, services, discounts and content by telephone and regular mail. You may at any time request the discontinuation of such communication and processing of personal data by withdrawing consent. You can withdraw your consent at any time through the contacts listed on www.sensilab.com/contact. |
|
General statistical processing of data about buyers and their orders and potential buyers (contacts) for the purposes of internal analyses of sales, repeated purchases, aggregate buyers' behaviour, advertising and business optimisation |
At Sensilab d.o.o. company we conduct general statistical processing of data about buyers and their orders, as well as potential buyers (contacts). Based on this processing we conduct internal analyses of sales, repeated purchases and aggregate buyers' behaviour and monitor and optimise our business efficiency and optimise our advertising, e.g.:
This type of statistical monitoring allows us to optimise our business and advertising in general and allows us to offer affordable products and services to users. This processing of personal data is based on the legitimate interest of the company to provide quality services and products to users. |
|
Access to your past purchases and other data by Sensilab call centre and stores consultants with the purpose of providing better services and offers |
When you place a call to our call centre (or our outbound call to you) or if you visit our store (if and when you independently identify yourself), our consultants will have access to your stored personal data and purchase history, based on which they will be able to provide better services and more relevant offers. This data processing is based on a legitimate interest of the company. If you do not want this data to be collected, you can stop this type of data processing at any time by sending us a written request to our e-mail address dpo@sensilab.com or by filling out the following form www.sensilab.com/dpo. |
|
Processing data about unclaimed remote orders with the purpose of fraud prevention |
At Sensilab d.o.o. company, we process data about sent and unclaimed remote orders based on our legitimate interest. By doing so, we determine if and which buyers disproportionately remotely order products with payment on delivery option and then do not claim these products, causing us business damage, which we wish to prevent. When we identify such buyers, we disable payment on delivery option for them, but they can still order products with immediate advance payment by pay cards or PayPal. |
|
Automated e-mail communication with the user based on her or his start of the online purchase process |
At Sensilab d.o.o. company, based on our legal interest, we occasionally send reminder e-mails to potential buyers that have put products into their shopping cart but never completed the purchase, with the purpose of reminding them to complete the purchase or offering them help or information in regards to doing so. You can stop this type of data processing at any time by either sending us a written request to our e-mail address dpo@sensilab.com or by filling out the following form www.sensilab.com/dpo. |
|
Basic customised communication (through e-mail, SMS, phone calls, mail, browser notifications, information at websites, social networks), with discounts, orders and content. |
Within the basic customised communication (through e-mail, SMS, phone calls, mail, information at websites, social networks) we try to present relevant offers, discounts and other content that might be of interest to you, based on your past interactions with us. For this, we use the following data about you:
During this process we do not use any type of automated or semi-automated profiling, we only collect suitable user sets for individual messages. We never focus on individual user's data, we only conduct aggregate processing of large groups. What messages you get from us is dependent on this data. You can stop this type of data processing at any time, either by clicking the unsubscribe link in received messages, by written request sent to this e-mail address dpo@sensilab.com or by filling out the following form: www.sensilab.com/dpo. |
|
Using the Facebook Custom Audiences advertising tool |
We at Sensilab d. o. o. use the Facebook Custom Audiences service. We use it based on the acquired agreement to communicate through customised offers and content based on the user's profile. The service functions in the following way:
This type of data processing can be stopped at any time by either sending us a written request to our e-mail address dpo@sensilab.com or by filling out the following form www.sensilab.com/dpo. |
|
Using Google Remarketing |
Using Google Remarketing allows us to let Google show you Google Ads (advertisements) for our products on other websites and in applications (including YouTube), based on the products you saw (the pages you visited) on Sensilab websites. Through cookies, Google “remembers” your device and your visit of a Sensilab website and the viewed product(s). When you visit a website or use the application which is part of Google Display Network, Google may show you an ad for a viewed product. To be able to use Google Remarketing, your name, email and phone number are processed and sent to Google, however in an anonymised form. Despite using Google Remarketing, Sensilab cannot tell that you made a purchase on Sensilab website by clicking on a certain Google Ad. The personal data for this purpose is only processed based on your consent, which you can revoke at any time by either sending us a written request to our e-mail address dpo@sensilab.com or by filling out form at www.slimjoy.com/dpo. |
|
Use of an online account and access to GDPR information |
We process your personal data in order to provide access to your user account, which allows you to access your personal information and regulate the consent given. You can also access past order information. We process personal information on the basis of legitimate interest. |
|
Communicating custom offers and content based on your user profile |
Based on consent, the provider can personalise the communication which is carried out through various communication channels (e-mail, phone calls, mail, browser notifications, website information, social networks). We want to present you with the best possible offers and content tailored to your needs, which is why we use your profile as the basis for personalised communication. We may use the following information for this purpose: Based on this user profile, it may then affect the content and offers you receive from us:
If you wish to revoke your consent at any point, you can terminate this data processing at any time via the unsubscribe link in your inbox or by sending a written request to dpo@sensilab.com or by using the following form www.sensilab.com/dpo. If you want access to non-personalised e-mails, you can subscribe to non-personalised informing here www.sensilab.com/dpo. |
|
Legal claims, rights protection and dispute resolution |
Data collection for the stated reason occurs in accordance with the law. |
|
Legal obligations |
We collect your information in order to fulfil our legal obligations, e.g. saving invoices for tax purposes. We process your data only to the extent necessary to comply with legislation. |
The provider will store your personal data only for the time necessary to realise the purpose for which the personal data was collected and further processed.
The personal data that are being processed on a legal basis the provider stores for the time period defined by law.
The personal data that are being processed based on a contract with the individual, the provider stores for the duration of the contract and 5 years after its expiration, unless there has been a dispute about the contract between the user and the provider. In this case, the provider stores data for 5 years after the finality of the court or arbitrary ruling or settlement or, if there was no judicial dispute, 5 years from the day of an amicable settlement.
The provider stores the data that are processed based on personal consent, until the revocation of such consent from the user. The provider deletes these data before objection only when the purpose of storing data had already been fulfilled.
After the end of the period of personal data being stored, the controller effectively and permanently erases or anonymises the personal data so that they cannot be linked to an individual.
|
Purpose of data processing |
Time period of data being stored |
|
Communication regarding our services or responding to requests |
6 months from the end of the communication |
|
Conclusion and fulfilment of obligations arising from entering a contract |
5 years from the execution of the contract |
|
Directly notifying customers about special offers, discounts and other content via e-mail or SMS |
Until revoked |
|
Directly notifying customers about special offers, discounts and other content by phone or regular mail |
Until revoked |
|
Access to past orders and other information by customer support consultants in order to provide a better service |
Until revoked |
|
Processing data on undelivered parcels with the purpose of fraud prevention |
5 years from the start of processing |
|
Automated e-mail communication with the user based on the beginning of the online buying process |
Until revoked |
|
Basic personalised communication (e-mail, SMS, phone calls, mail, browser notifications, website information, social networks) with personalised offers and content |
Until revoked |
|
Facebook Custom Audiences Advertising Tool |
Until revoked |
|
Google Remarketing |
Until revoked |
|
Using an online account |
Until revoked |
|
Access to specific information on the website |
Until revoked |
|
Personalised e-magazines |
Until revoked |
|
Market communication using user profiles |
Until revoked |
The provider may entrust some tasks related to the processing of personal data to others (contractual processors). Contractual processors may process confidential data exclusively in the name of the provider, within limits of the provider’s mandate (a written contract or other legal act) and according to purposes as defined in this privacy policy.
Contractual processors that the controller transmits personal data are:The provider will not forward your personal information to third unauthorised parties.
Contractual processors can only process personal data within the framework of the controller’s instructions and must not use it to pursue any interests of their own.
The controller and recipients of personal data do not transmit personal data to third countries (outside of member countries of the European economic area – members of EU and Iceland, Norway and Liechtenstein) and to international organisations, except the USA - all contractual processors in the USA are in the Privacy Shield programme.
You are in control of any information you give out about yourself. If you decide you do not wish to share your data, we may not be able to provide you with certain services.
Individuals that wish to unsubscribe from the e-newsletter, please notify us through our e-mail address support@sensilab.com. If there are any changes to your personal information (zip code, e-mail address, physical address, phone number), please notify us through our e-mail address support@sensilab.com.
Whenever you visit our website, the general, non-personal information (browser users, number of visits, the average duration of the visit, pages visited) are being automatically recorded (not as a part of registration). This information is used to measure the attractiveness of our website and to improve the content and usability. Your information is not subject to further examination and is not disclosed to a third party.
Cookies are small pieces of data that are temporarily stored on your hard drive that allow our website to recognize your computer the next time you visit the website. The provider uses cookies only to gather information concerning the use of the website and to optimise online advertising activities. Advertising cookies monitor the individual’s usage of the provider’s website unless the individual does not agree to website cookie use. You can read more about cookies and how they’re used here.
The provider is strongly committed to ensuring personal data security. Your data is, at all times, protected from loss, destruction, falsification, manipulation and unauthorised access and unauthorised disclosure.
In order to protect personal data, we take organisational and technical measures, such as:
Minors under 16 years of age should not transmit any personal data to websites without the permission (consent or approval) of a parent or a legal guardian. The provider will never knowingly collect personal information from minors (under 16 years of age) or in any way use or disclose them to an unauthorised third party without their parent’s or legal guardian’s permission.
The above does not affect the general law of contract of member states, like regulations about validity, drawing up or effects of the contract regarding minors.
Bearing in mind the available technology, the provider will show reasonable efforts to verify that a parent of a legal guardian gave or approved consent.
If you have any questions about our privacy policy or processing in regards to your personal data, you can contact us. Write to us at support@sensilab.com. Based on your request, we will notify you about the requested information or fulfil your request ( in accordance with applicable legislation).
As an individual, you have the following rights regarding fair and transparent processing, based on regulation:
The right to withdraw consent: if you have, as an individual, consented to the processing of personal data (for one or more purposes), you have the right to withdraw your consent at any time, without affecting the lawfulness of processing based on consent before its withdrawal.Consent can be withdrawn through a written statement that is sent to the provider to one of the contacts at the provider’s website www.sensilab.com/contact.
Withdrawal of consent for personal data processing has no negative consequences or sanctions for the individual. However, it is possible that the controller may not be able to offer one or more of its services after the withdrawal of consent if those services cannot be performed without personal data (e.g. the benefit club or customised communication).
The right to access personal data: as an individual, you have the right to obtain from confirmation from the provider (processor of personal data) as to whether or not your personal data are being processed, and, where that is the case, access to the personal data and the following information: the purposes of the processing, the categories of personal data concerned, its users, the period for which the personal data will be stored, or the criteria used to determine that period, the right to request rectification or erasure of personal data or restriction of or objection to processing of personal data, the right to lodge a complaint with a supervisory authority, the source of the data if the data were not collected from you, the existence of automated decision-making, including profiling and meaningful information about the logic involved, as well as the significance and the envisaged consequences of such processing for you, in accordance to Article 15 of GDPR.
The right to rectify personal data: as an individual, you have the right to obtain from the provider without undue delay the rectification of inaccurate personal data concerning you. Taking into account the purposes of the processing, you have the right to have incomplete personal data completed, including by means of providing a supplementary statement;
The right to deletion of personal data (“the right to be forgotten”): you have the right to obtain from the provider without undue delay the deletion of your personal data when one of the below reason exists:
(a) the personal data are no longer necessary in relation to the purposes for which they are collected or otherwise processed,
(b) you have withdrawn your consent, and there is no legal basis for further processing,
(c) you have objected to the processing of your personal data, and there are no overriding legitimate grounds for the processing,
(d) your personal data have been unlawfully processed,
(e) ) the personal data have to be erased for compliance with a legal obligation in Union or Member State law to which the provider is subject,
(f)the personal data has been collected in relation to the offer of an information society.
As an individual under certain circumstances, as defined in Article 17, paragraph 3, you do not have the right to data deletion;
The right to restriction of processing: as an individual, you have the right to obtain from the provider restriction of processing where one of the following applies:
(a) you contest the accuracy of the personal data for a period enabling the provider to verify the accuracy of the personal data,
(b) the processing is unlawful and you oppose the erasure of the personal data and request the restriction of their use instead,
(c) the provider no longer needs the personal data for the purposes of the processing, but they are required by you for the establishment, exercise or defence of legal claims,
(d)you have objected to processing pending the verification whether the legitimate grounds of the provider override yours;
The right to data portability: you have the right to receive the personal data concerning you, which you have provided to the provider, in a structured, commonly used and machine-readable format and have the right to transmit those data to another controller without hindrance from the provider to which the personal data have been provided, where:
(a) the processing is based on consent or on a contract; and
(b) the processing is carried out by automated means.
In exercising your right to data portability, you have the right to have your personal data transmitted directly from one controller (provider) to another, where technically feasible;
The right to object to data processing: as an individual, you have the right to object, on grounds relating to your particular situation, at any time to processing of your personal data that is necessary for the performance of a task carried out in the public interest or in the exercise of official authority vested in the provider (Article 6 (1), point (e) of GDPR), processing is necessary for the purposes of the legitimate interests pursued by the provider or by a third party (Article 6 (1) point (f) of GDPR), including profiling based on the data; the provider shall no longer process your personal data unless the provider demonstrates compelling legitimate grounds for the processing which override your interests, rights and freedoms or for the establishment, exercise or defence of legal claims.
Where personal data are processed for direct marketing purposes, you have the right to object at any time to processing of your personal data for such marketing, which includes profiling to the extent that it is related to such direct marketing; where you object to processing for direct marketing purposes, the personal data shall no longer be processed for such purposes.
Where data are processed for scientific or historical research purposes or statistical purposes, you have the right, on grounds relating to your particular situation, to object to the processing of your data, unless it is necessary for the performance of a task carried out in the public interest;
The right to lodge a complaint with a supervisory authority: without prejudice to any other administrative or judicial remedy, you have the right to lodge a complaint with a supervisory authority, in particular in the Member State of your habitual residence, place of work or place of the alleged infringement if you consider that the processing of your personal data infringes data protection regulations.
Without prejudice to any other administrative or non-judicial remedy, you have the right to an effective judicial remedy, against a legally binding decision of a supervisory authority concerning it, as well as where the supervisory authority which is competent does not handle a complaint or does not inform you within three months on the progress or outcome of the complaint lodged. Proceedings against a supervisory authority shall be brought before the courts of the Member State where the supervisory authority is established.
The individual may address all her or his requests regarding personal data in written form to the provider, through one of the contacts at the website https://www.sensilab.com/contact.
In order to ensure reliable identification in case of a user exercising his or her rights regarding personal data, the provider may request additional data from the user and shall not refuse to act on the request of the individual, unless the provider demonstrates that it is not in a position to identify the user.
The provider must, by user’s request to exercise his or her rights in regards to data processing, provide information without undue delay and in any event within one month of receipt of the request.
In the case of a personal data breach, the provider is obligated to notify the supervisory authority without undue delay, unless the provider is able to demonstrate that the data breach is unlikely to result in a risk to the rights and freedoms of individuals. When there is a suspicion of a criminal offence, the provider is obligated to notify the police and/or prosecutor.
In the case of a breach that is likely to result in a high risk to the rights and freedoms of natural persons, the provider is obligated to notify the individual immediately or, if that’ is not possible, without undue delay. The notification should be in clear and comprehensible language.
Through our website, you can access the following web pages, which the provider utilizes in their work:
Each of these social networks, when providing their services, acts in accordance with their terms of use and privacy policies. Sensilab does not assume any liability with respect to the use of social networks that the user may access through its website. Questions and claims need to be addressed to individual social networks.
The privacy policies are available at the links below:
All changes in our privacy policy will be published on this website.
Updated: 28.06.2023
| sensilab.com | popup_displayed | Sessions | Means that the display opens |
| sensilab.com | frontend | Sessions | Session ID |
| sensilab.com | cookieOK | 1 year | Means that the user on a site agrees with the use of cookies |
| sensilab.com | popups | 1 year | |
| sensilab.com | external_no_cache | Sessions | System cookies to optimize servers |
| sensilab.com | cookieOK | 1 year | |
| sensilab.com | user_allowed_save_cookie | 1 year | Means that users agree to the transfer of cookies to the site |
| sensilab.com | zte2095 | Sessions | Cookie allows chat |
| sensilab.com | __zlcmid | 1 year | Cookie allows chat |
| CloudFlare | __cfduid | 1 year | For a faster location and transfer of image material on the page. After CloudFlare disable the operation cookies block access via IP. Does not use / has no personal data of the user. |
| New Relic | bam.nr-data.net | Sessions | New Relic provides a platform to control the operation of the website on mobile applications. |
| PayPal | [various] | Sessions | This cookie allows a unique ID between payment with PayPal and our shopping cart. |
| Adform | C | 1 Month | Targeting/Advertising |
| Adform | cid | 2 Months | Targeting/Advertising |
| Adform | uid | 2 Months | Targeting/Advertising |
| AppNexus Inc | sess | Sessions | Targeting/Advertising |
| AppNexus Inc | anj | 3 Months | Targeting/Advertising |
| AppNexus Inc | uuid2 | 3 Months | Targeting/Advertising |
| Bing | ANONCHK | Sessions | Targeting/Advertising |
| Bing | MR | 6 Months | Targeting/Advertising |
| Bing | MUID | 2 years | Targeting/Advertising |
| test_cookie | Sessions | Targeting/Advertising | |
| id | 2 years | Targeting/Advertising | |
| Gravity | gr_reco | 1 year | Targeting/Advertising |
| Improve Digital | tuuid | 2 years | Targeting/Advertising |
| Improve Digital | um | 2 years | Targeting/Advertising |
| Improve Digital | umeh | 2 years | Targeting/Advertising |
| IPONWEB | c | 2 years | Targeting/Advertising |
| IPONWEB | tuuid | 2 years | Targeting/Advertising |
| Media Innovation Group | id | 1 Month | Targeting/Advertising |
| Media Innovation Group | mdata | 1 Month | Targeting/Advertising |
| Media Innovation Group | syncdata_AN | 1 Month | Targeting/Advertising |
| Mojn | idt | Permanent | Targeting/Advertising |
| Mojn | tmpagid | Permanent | Targeting/Advertising |
| Mojn | ls | Permanent | Targeting/Advertising |
| Mojn | rtt | Permanent | Targeting/Advertising |
| Mojn | _mojn | Permanent | Targeting/Advertising |
| OpenX | i | 1 year | Targeting/Advertising |
| Pubmatic | KRTBCOOKIE_466 | 3 Months | Targeting/Advertising |
| Pubmatic | PUBMDCID | 3 Months | Targeting/Advertising |
| RadiumOne | RA1balancer | Permanent | Targeting/Advertising |
| RadiumOne | ra1_sgm | 1 year | Targeting/Advertising |
| RadiumOne | ra1_sgm_1097308745 | 1 year | Targeting/Advertising |
| RadiumOne | ra1_sgm_1118270538 | 1 year | Targeting/Advertising |
| RadiumOne | ra1_sgm_1426802167 | 1 year | Targeting/Advertising |
| RadiumOne | ra1_sgm_1702745841 | 1 year | Targeting/Advertising |
| RadiumOne | ra1_sgm_1795933472 | 1 year | Targeting/Advertising |
| RadiumOne | ra1_sgm_1973119023 | 1 year | Targeting/Advertising |
| RadiumOne | ra1_sgm_2107935356 | 1 year | Targeting/Advertising |
| RadiumOne | ra1_sgm_328720634 | 1 year | Targeting/Advertising |
| RadiumOne | ra1_sgm_631030195 | 1 year | Targeting/Advertising |
| RadiumOne | ra1_sgm_799597431 | 1 year | Targeting/Advertising |
| RadiumOne | ra1_sid | 1 year | Targeting/Advertising |
| RadiumOne | ra1_uid | 1 year | Targeting/Advertising |
| Rubicon Project | c | Sessions | Targeting/Advertising |
| Rubicon Project | put_1986 | 1 Month | Targeting/Advertising |
| Rubicon Project | put_2760 | 1 Month | Targeting/Advertising |
| Rubicon Project | rpb | 1 Month | Targeting/Advertising |
| Rubicon Project | khaos | 6 Months | Targeting/Advertising |
| Rubicon Project | rpx | 1 Month | Targeting/Advertising |
| Yahoo | B | 2 years | Targeting/Advertising |
| datr | 2 years | Targeting/Advertising | |
| x-src | Sessions | Targeting/Advertising | |
| reg_fb_ref | Sessions | Targeting/Advertising | |
| reg_fb_gate | Sessions | Targeting/Advertising | |
| Addthis | uvc | Sessions | |
| Addthis | page_services | indefinitely | |
| Addthis | vc | 2 years |
| Optimizely | optimizelyPendingLogEvents | Sessions |
| Optimizely | optimizelyBuckets | Permanent |
| Optimizely | optimizelyEndUserId | Permanent |
| Optimizely | optimizelySegments | Permanent |
| Optimizely | bucket_map | Permanent |
| Optimizely | end_user_id | Permanent |
| _gat | Sessions | |
| _ga | 2 years | |
| __utma | 2 years | |
| __utmb | Sessions | |
| __utmz | 6 Months | |
| __utmv | 2 years | |
| __utmc | Sessions |
Contact us online
100% satisfaction guarantee
Free delivery above £40
Contact us
support@sensilab.com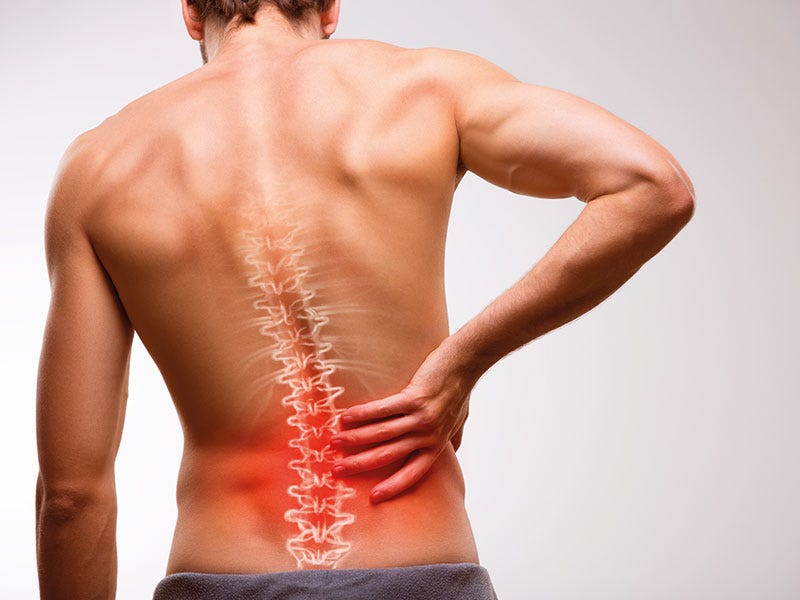
When your back hurts, your concentration decreases and you feel restricted. The causes can be strained muscles and ligaments or wear and tear of the spine and intervertebral discs. Quick help is needed, if possible without tablets, so that the pain does not get worse. This is why it is so important to strengthen the back muscles and thus prevent pain directly.
We owe the upright walk to the spine. It stabilizes the back and is also responsible for our ability to stand, walk, jump and sit.
The spinal column consists of 33 to 34 vertebrae, 24 of which are mobile and between 9 and 10 are joined together. It runs from the neck over the back down to the buttocks. It can be divided into 5 sections:
The individual vertebrae: The vertebrae of the cervical spine, thoracic spine and lumbar spine have the same bony structure, they only differ in shape and size. Each vertebra consists of a vertebral body, to which the vertebral arch is attached. The cavity that is created in the middle of the vertebrae is called the spinal canal. The spinal cord is well protected in it. The individual vertebral bodies are connected by movable joints. The cartilaginous discs keep these joints mobile.
The double S shape: The natural curvature of the spine has an important function. It cushions forces that arise from movement: for example when running or jumping. The curvature therefore makes our spine more stable and resilient.
Back pain can have far-reaching causes: from drafts to psychological strain, stress to a serious malposition of the spine. A distinction is made between acute and chronic back pain.
Badly trained back and abdominal muscles are often responsible for acute back problems. If the muscles are overstrained, tension in the individual muscle fibres, the so-called trigger points, can be felt. The result: pain.
Acute back problems can usually be clarified quickly: The causes are easy to understand and are eliminated after some time. Circumstances that may currently be more demanding and therefore cause stress or even anxiety can result in symptoms such as pain and tension. If your pain lasts longer than 6 weeks, it is no longer called acute back pain but chronic pain.
Chronic back problems are often not directly perceived as such. They accompany you through the day and almost belong to it. The triggers are often malpositions of the spine, hard physical work, or imbalances, such as the permanent one-sided carrying of heavy bags.
The overview shows a few typical symptoms of back pain and their causes:
The physically active: cleaning staff, craftsmen and women, construction workers, housewives or househusbands
Very often physically hard working people have to lift, push, carry or generally put their body into positions that are unhealthy in the long run. A wrong posture then leads to pain - especially in the back. The pain is felt in the lower and upper as well as in the neck and shoulder area.
The sitters: Office, truck drivers, cashiers
This group also often strains its back without knowing it. Sitting at a desk or with your hands on the steering wheel for hours is not good for your body. Also here: The wrong posture, too little stretching and hardly any compensation cause back pain.
The persistent ones: Hairdressers, bakers, caterers
Standing for long periods of time also works on the back. The lower area in particular is subject to heavy strain. Again the posture plays a decisive role. In general, the body needs variety: sitting, standing, lying, movement, everything is important. Depending on the occupational group, compensation should be provided.
The older generation: The likelihood of suffering from back pain becomes more regular with age. The lifelong strain on the spine does not go unnoticed. Vertebrae can slip or even break and signs of wear and tear of the joints occur more frequently. It is therefore true that you should take more care of yourself and your back as you get older.
+++ Staying fit in old age - why sport is so important now +++
The young generation: Back pain does not only plague older people. Young people, even children, complain about back problems. For many, back pain can be attributed to a lack of physical exercise. Others have a dysbalance, for example because of a school bag that is too heavy. In some cases, however, it is also due to hormones and growth.
Although back pain can affect any sex, women are more frequently affected than men, according to a study by the Robert Koch Institute.
Menstruation, pregnancy/birth, menopause - hormones play a decisive role. Menstruation or menstruation can trigger abdominal pain, which is often associated with back pain or low back pain. Of course, pregnancy because of the heavy belly and birth because of the great strain should not be underestimated. In both cases a lot of energy and strength is demanded from the body, which is extremely hard on the back. In the menopause, the hormonal balance generally changes, and lower back pain is often the result.
Too many kilos can also cause back problems, especially in the lower back: back pain. This is mainly because the excess weight presses against the muscles and the body is under constant tension.
Every now and then everyone has to lift something heavy or carry it across the room. What is most important is the "how". Deliberately get down on your knees and keep your back straight. The back must not be bent. In the long run you will prevent pain and especially chronic problems.
No hollow back and no hunchback. When sitting, always make sure that you form a straight back. Especially people who sit a lot in everyday life should consciously pay attention to how they do it. Both feet should be able to rest on the floor. You should be able to rest your elbows on the desk. It is also important that your screen is set at eye level. The more often movement units can be introduced in between, the better. It is therefore a good idea to get up every now and then and take a short walk, e.g. to the printer, the kitchenette or the window.
+++ Fit and healthy - and that also at the workplace +++
Those who do not do sport are not at a disadvantage immediately. Of course, being active in sports helps enormously, prevents many diseases and protects against back pain. Nevertheless, not everyone is as fit when they are on the move. Nevertheless: exercise helps. Walks, fast walks and above all stretching exercises can spare your back pain.
Do stretch exercises first thing in the morning and whenever you have the opportunity. Stretch your back and make yourself long. You can do this standing or sitting. Stretch your arms in the air and first pull your right arm higher so that you feel a stretch on your right side of your body. Do the same with your left arm. Imagine you are picking apples from a tree.
A good posture is beautiful and above all healthy for the back. Align your body as straight as possible. Shoulders, hips, pelvis, knees and feet should point straight ahead. Your neck serves as an extension of your spine. Relax your shoulders and neck, do not pull them up.
If you sleep well, back pain is automatically prevented. When choosing your mattress, make sure that it is neither too soft nor too hard. Get advice and try out the mattress before you buy it.
Your sleeping position also affects your back. It is best to change between the supine and lateral position. The body is supplied with blood and the spine is balanced.
Food supplements can strengthen your back from the inside out. These two are particularly beneficial for a relaxed back: Magnesium supports normal muscle function. Back problems caused by muscle tension can be better resolved. Joint Vital can have a strengthening effect on your joints. Healthy and flexible joints prevent wear and tear, which in turn can cause back pain.
The rotation in the spine has a relieving effect. If you experience pain while doing this, make sure you relax when you exhale. Repeat the exercise 5 times with each leg and hold the position for about 10 seconds.
Alternative: Perform the exercise in the opposite direction. When you lift your right leg, the left arm is raised and vice versa.
The main purpose of the exercise is to strengthen the back and stretch the spine. It is best to do the exercise for 10-20 seconds. Then put your arms and legs down for about 10 seconds and repeat the whole thing about 5-10 times.
The lower back is stretched and relaxed. Do the exercise for about 20 seconds on each side and repeat this twice for each leg.
Hold this position for 5 seconds, breathe evenly. As you exhale, you should feel a stretch in your upper back and neck. Repeat the exercise 3 times.
You'd better start right away. Have fun, your back will thank you.

